Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (Gramin)
- Ministry – Ministry of Rural Development
- Launched in 2015 as Housing for All by 2022.
- It is a social welfare programme, created by the Indian Government, to provide housing for the rural poor in India.
- The rural housing scheme Indira Awas Yojana has been revamped to Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana – Gramin and approved during March 2016.
- The cost of unit assistance is to be shared between Central and State Governments in the ratio 60:40 in plain areas and 90:10 for North Eastern and hilly states.
- Financial assistance worth ₹120,000 (US$1,700) in plain areas and ₹130,000 (US$1,800) in difficult areas (high land area) is provided for construction of houses.
- These houses are equipped with facilities such as toilet, LPG connection, electricity connection, and drinking water [convergence with other schemes e.g. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan toilets, Ujjwala Yojana LPG gas connection, Saubhagya Yojana electricity connection, etc.].
- The houses are allotted in the name of the woman or jointly between husband and wife.
- The beneficiary is entitled to 90 days of unskilled labour from MGNREGA.
- The beneficiary would be facilitated to avail loan of up to Rs.70,000/- for construction of the house which is optional.

Ganga Gram Project
- Ministry – Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation
- Launched on 23rd december, 2017.
- The ‘Ganga Gram’ project as part of the government’s clean Ganga mission, named Namami Gange, for holistic sanitation development in 4,470 villages on the banks of the river.
- Rural habitation and villages situated in vicinity of River Ganga contribute a significant pollution load to the river on account of open defecation, dirty water and solid wastes from the individual households entering the river through village drains and nallahs.
- Therefore, rural based pollution load in Ganga River is sought to be addressed through development of Ganga Grams.
Vision:
- To develop model village, that will exhibit itself as comprehensive and harmonious package of economic, historic, cultural and sanitized unit, on banks of Ganga, which is self –sustaining. Promoting brand “Ganga” in its handicraft, organic farm produce and tourism will be other spin offs.
Components of Ganga Grams:
- Making village Open Defecation Free, ODF.
- Proper management of village waste draining into river Ganga
- Proper disposal of solid waste.
- Water conservation activities including rain water harvesting/ground water recharge/maintain of well and ponds, promotion of sprinkler irrigation
- Encourage plantation of medicinal plants and promotion of organic farming
- Construction of crematorium
- Promotion of tourism
- Coordination between various Central and State Governments sponsored schemes and their implementation on priority in Ganga Grams

National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction
- Ministry – Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has prepared a National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR) for 2018-2023 so as to focus on preventive education, awareness generation, identification, counselling, treatment and rehabilitation of drug dependent persons and training and capacity building of the service providers through collaborative efforts of the Central and State Governments and Non-Governmental Organizations.
- Article 47 of the Constitution provides that “The State shall regard the raising of the level of nutrition and the standard of living of its people and the improvement of public health as among its primary duties and, in particular, the State shall endeavor to bring about prohibition of the consumption except for medicinal purposes of intoxicating drinks and of drugs which are injurious to health.”
- India is a signatory to the three UN Conventions namely, Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961, Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971 and Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988.
- The Government of India has enacted the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act in the year 1985 to make stringent provisions for the control and regulation of operations relating to narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
Objectives of NAPDDR
- Create awareness and educate people about the ill-effects of drugs abuse on the individual, family, workplace and the society at large and reduce stigmatization of and discrimination against, groups and individuals dependent on drugs in order to integrate them back into the society;
- Develop human resources and build capacity for working towards these objectives;
- Facilitate research, training, documentation, innovation and collection of relevant information to strengthen the above mentioned objectives;
- Provide for a whole range of community based services for the identification, motivation, counselling, de-addiction, after care and rehabilitation for Whole Person Recovery (WPR) of addicts;
- Formulate and implement comprehensive guidelines, schemes, and programmes using a multiagency approach for drug demand reduction;
- Undertake drug demand reduction efforts to address all forms of drug abuse;
- Alleviate the consequences of drug dependence amongst individuals, family and society at large.
The National Institute of Social Defence (NISD), New Delhi, an autonomous body under the administrative control of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, is the nodal training and research Institute for interventions in the area of Social Defence.
Womaniya on Government e Marketplace
- Ministry – Ministry of Commerce & Industry
- An initiative to enable women entrepreneurs and women self-help groups [WSHGs] to sell handicrafts and handloom, accessories, jute and coir products, home décor and office furnishings, directly to various Government ministries, departments and institutions.
- The initiative seeks to develop women entrepreneurship on the margins of society to achieve gender-inclusive economic growth.
- Since women tend to invest up to 90 percent of their earnings back in their families to provide better nutrition, health care and education to their children, economic empowerment of women is a step in the direction of poverty alleviation.
- The initiative aligns with Government’s initiatives for MSMEs, especially to reserve 3 percent in government procurement from women entrepreneurs.
- Womaniya on GeM will spur hyper-local economic opportunities for women entrepreneurs and address goals and objectives under United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 5: Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls.
- Government e Marketplace is a 100 percent government owned company setup under the aegis of Ministry of Commerce and Industry for procurement of common use goods and services by Government ministries, departments and CPSEs.
Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY)
- Ministry – Ministry of Mines
- This programme meant to provide for the welfare of areas and people affected by mining related operations.
- The most productive mining areas in the country are largely areas inhabited by scheduled tribes.
- They also are mainly located in the areas covered by the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution.
- The PMKKKY is, therefore, very sharply focused on safeguarding the health, environment and economic conditions of the tribals and providing them with opportunities to benefit from the vast mineral resources that are extracted from the areas where they live.
Objectives
The overall objective of PMKKKY scheme include
- to implement various developmental and welfare projects/programs in mining affected areas, and these projects/ programs will be complementing the existing ongoing schemes/projects of State and Central Government;
- to minimize/mitigate the adverse impacts, during and after mining, on the environment, health and socio-economics of people in mining districts; and
- to ensure long-term sustainable livelihoods for the affected people in mining areas.
- The Pradhan Mantri Khanij Kshetra Kalyan Yojana (PMKKKY) will be implemented by the District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) of the respective districts using the funds accruing to the DMF.
- The Mines and Minerals (Development & Regulation) Amendment Act, 2015, mandated the setting up of District Mineral Foundations (DMFs) in all districts in the country affected by mining related operations.
Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (SAUBHAGYA)
- Ministry – Ministry of Power
- launched on September 25, 2017.
- It is to provide energy access to all by last mile connectivity and electricity connections to all remaining un-electrified households in rural as well as urban areas to achieve universal household electrification in the country.
- The electricity connection to households include release of electricity connections by drawing a service cable from the nearest pole to the household premise, installation of energy meter, wiring for a single light point with LED bulb and a mobile charging point.
- In case the electricity pole is not available nearby from household for drawing service cable, the erection of additional pole along with conductor and associated accessories shall also be covered under the scheme.
- The States and Union Territories are required to complete the works of household electrification by the 31st of December 2018.
Features
- Access to electricity to all willing households
- Substitution to Kerosene
- Improvement in Health Services
- Improvement in Communications
- Improvement in Public Safety
- Increased Job Opportunities
- Better Quality of Life, especially for Women, in Daily Chores
The Rural Electrification Corporation Limited (REC) the nodal agency for the operationalisation of the scheme throughout the country.
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE SAUBHAGYA ELECTRICITY SCHEME
- The scheme is launched on the occasion of the birth centenary celebration of Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya on 25th September.
- Scheme aims to achieve 24×7 power for all by 2019 by providing electricity connection to each household across the country.
- Scheme will provide subsidy on equipment such as transformers, wires and meters.
- Ministry of Power would be the implementing authority of the scheme.
- Power connection will be provided in both rural and urban areas of the country.
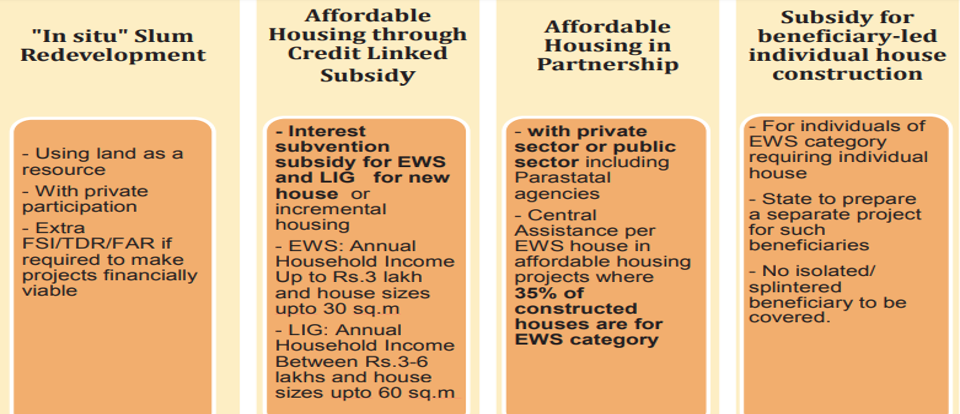
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Urban (PMAY-U)
- Ministry – Ministry of Housing and Urban Poverty Alleviation (MoHUPA)
- For ensuring housing for all in urban areas was launched on 25th June 2015 for implementation during 2015-2022.
- The mission addresses urban housing shortage among the EWS/LIG and MIG categories including the slum dwellers by ensuring a pucca house to all eligible urban households by the year 2022, when nation completes 75 years of its independence.
- The State Level Nodal Agencies (SLNAs), Urban Local Bodies (ULBs), Central Nodal Agencies (CNAs) and Primary Lending Institutes (PLIs) are important pillars which contribute to implementation & success of PMAY(U).
- The mission focuses to cover the entire urban area consisting of all statutory towns and planning areas including Urban Development Authorities (UDAs) notified with respect to the Statutory Towns which surround the concerned municipal areas.
- All houses under PMAY(U) have facilities like electricity, water supply, kitchen and toilet.
- The mission promotes women empowerment by providing the ownership of houses in name of female member or in joint name.
- Preference is also given to persons with disabilities, ST/ SC/ OBCs/ Minorities and Transgender. A
- PMAY(U) house ensures dignified living along with sense of security and pride of ownership to the beneficiaries.
Coverage and Duration
- All 4041 statutory towns as per Census 2011 with focus on 500 Class I cities would be covered in three phases as follows:
- Phase I (April 2015 – March 2017) to cover 100 Cities selected from States/UTs as per their willingness.
- Phase II (April 2017 – March 2019) to cover additional 200 Cities •
- Phase III (April 2019 – March 2022) to cover all other remaining Cities
- The mission will support construction of houses upto 30 square meter carpet area with basic civic infrastructure.
Implementation Methodology
- The Mission will be implemented through four verticals giving option to beneficiaries, ULBs and State Governments. These four verticals are as below:
- A comprehensive robust MIS system is in place.
- The MIS is equipped with Geo-tagging features and integrated with BHUVAN Portal of National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) and BHARAT MAP of National Informatic Centre (NIC) for monitoring the progress of construction of houses.
- A Technology Sub-Mission (TSM) under the Mission has been set up to facilitate adoption of modern, innovative and green technologies and building material for faster and quality construction of houses.
- Under Accelerator Affordable Sustainable Housing Accelerators- India (ASHA-India) initiative, incubation and acceleration support will be provided to potential future technologies that are not yet market ready (pre-prototype applicants) or to the technologies that are market ready (post prototype applicants) respectively.
- Ministry has launched a Global Housing Technology Challenge- India (GHTC-India) to get the best globally available construction technologies through a challenge process and to enable paradigm shift in the housing construction sector.
- Prime Minister of India inaugurated the Construction Technology India- 2019, a global Expo-cum-Conference which was organized on 2-3 March 2019 in New Delhi. Prime Minister declared the year 2019-20 as the ‘Construction Technology Year’.
- New, Affordable, Validated, Research Innovation Technologies for Indian Housing (NAVRITIH) Certificate course on Alternate Technologies is also to be launched in consultation with MoHRD.
BharatMala Pariyojana
- Ministry of Road Transport & Highways
- It is a new umbrella program for the highways sector that focuses on optimizing efficiency of freight and passenger movement across the country by bridging critical infrastructure gaps.
- Through effective interventions like development of Economic Corridors, Inter Corridors and Feeder Routes, National Corridor Efficiency Improvement, Border and International connectivity roads, Coastal and Port connectivity roads and Green-field expressways.
- The implementation of a pan-nation scheme to improve the road network was the idea of the PM.
Highlights of Bharatmala Pariyojana
- Improvement in efficiency of existing corridors through development of Multimodal Logistics Parks and elimination of choke point
- Enhance focus on improving connectivity in North East and leveraging synergies with Inland Waterways
- Emphasis on use of technology & scientific planning for Project Preparation and Asset Monitoring
- Delegation of powers to expedite project delivery – Phase I to complete by 2022
- Improving connectivity in the North East
KEY FEATURES OF THE SCHEME
- Improving the quality of roads – The launch of the scheme has been done for bring a new wave of development in the nation in the form of well-maintained and developed roads. Under this project, the construction of roads, in all parts of the nation will be undertaken.
- Total road construction – As per the draft of the scheme, government and the ministry will strive to complete new roads, which will add up to a whopping 34, 800 kms.
- Integrated scheme – The Bharatmala is the name that is given to the road development and it will include many other related schemes as well. With the completion of all the schemes, the overall success of the scheme will be guaranteed.
Total tenure of the program – The central government has the plans of finishing the scheme within a span of five years. Thus, all is set for finishing the first phase before the end of 2022.
- Segmentation in phases – Due to the sheer magnitude and spread of the scheme, it will be divided into seven distinct phases. As of now, the first phase in under construction.
- Constriction on a daily basis – To finish the first phase in time, the respective department has made efforts of constructing at least 18 km of path on a daily basis. To beat the clock, continued efforts are being made to raise it to 30 km/day.
- Different categories of road construction – It has been highlighted in the official draft of the scheme that to provide better connectivity, the construction of various categories of roads will be undertaken.
Multi-source of finding – One source will not be enough for funding a mammoth project. Thus, the government will have to depend on other sources for generating adequate money to meet the expenses.
Budget Allocation
- A total of around 24,800 kms are being considered in Phase I of Bharatmala.
- In addition, Bharatmala Pariyojana phase -I also includes 10,000 kms of balance road works under NHDP, taking the total to 34,800 kms.
- Bharatmala Phase I – is to be implemented over a five years period of i.e. 2017-18 to 2021-22.
BHARATMALA PROJECT CATEGORY
- Economic Corridor – As per the guidelines of the road construction project, the construction of 9000 kms of Economic Corridors will be undertaken by the central government.
Feeder Route or Inter Corridor – The total length of the roads, which fall under the Feeder Route or Inter Corridor category, is a whopping 6000 kms.
- National Corridor Efficiency Improvement – 5000 kms of roads, constructed under the scheme will fall in the category of National Corridor for the better connection between roads.
- Border Road and International Connectivity – Connecting the cities and remote areas, which are situated in the border regions, the project has kept provision for constructing 2000 kms roads that fall in the Border Road or International Connectivity category.
- Port Connectivity and Coastal Road – To connect the areas that are dotted along the shorelines and important ports, the central government has ordered the construction of 2000 km of roads.
- Green Field Expressway – The main stress will be given on the construction and development of Green Field Expressway for better management of traffic and freight.
Balance NHDP Works – Under the last segment, the project will see a construction and maintenance of about 10,000 kms of new roads.
Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana
- Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas
- PMUY was launched r on May 1, 2016 at Ballia in Uttar Pradesh.
- In order to provide clean cooking fuel to every poor households especially in rural areas, the Government had launched “Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana” to provide deposit-free LPG connections to 5 crore women belonging to the Below Poverty Line (BPL) which has now been enhanced to 8 crore.
- Goal to provide environment friendly clean cooking fuel (LPG) to women of rural areas in order to get rid of health hazards faced by them by using traditional hazardous fuel.
- According to WHO estimates, about 5 lakh deaths in India alone due to unclean cooking fuels.
- Most of these premature deaths were due to non-communicable diseases such as heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer.
- Indoor air pollution is also responsible for a significant number of acute respiratory illnesses in young children.
- According to experts, having an open fire in the kitchen is like burning 400 cigarettes an hour.
As part of Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana scheme for the PMUY beneficiaries to enable them to combat COVID 19 crisis, availability of up to 6 refills for 14.2 kg cylinders and advance Retail Selling Price being transferred by OMCs to the PMUY customer’s bank account, which can be withdrawn to obtain the refill from the distributor has been announced.
The salient features of the PMUY Scheme are as under:-
- LPG Connection is released in the name of adult woman of the BPL Family, subject to the condition that no LPG connection exists in the name of any family member of the household.
- The Scheme covers the cash assistance upto Rs. 1600/- for providing new LPG connection and this cash assistance is provided by the Central Government.
- The customer bears the cost of Hot plate and purchase of first refill.
- The customers have option to take Hot plate on purchase of first refill or both on loan basis from zero interest rate and the same is recovered through subsidy received by the beneficiary.
- No recovery of loan is effecting for initial 6 refills.
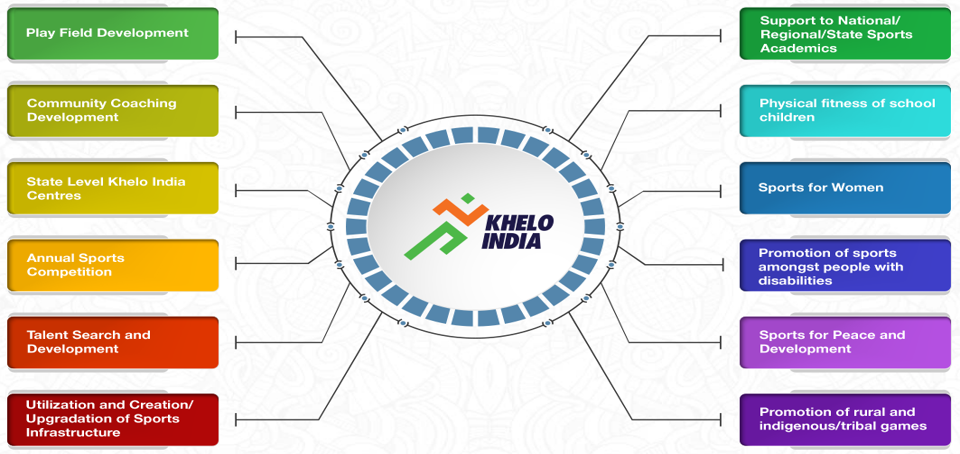
Khelo India Programme
- Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- The Khelo India programme has been introduced to revive the sports culture in India at the grass-root level by building a strong framework for all sports played in our country and establish India as a great sporting nation.
- Talented players identified in priority sports disciplines at various levels by the High-Powered Committee will be provided annual financial assistance of INR 5 lakh per annum for 8 years.
- Khelo India School Games are a part of the Khelo India programme.
- Under-17 athletes have been invited to participate across 16 disciplines, which are as follows: Archery, Athletics, Badminton, Basketball, Boxing, Football, Gymnastics, Hockey, Judo, Kabaddi, Kho-Kho, Shooting, Swimming, Volleyball, Weightlifting, and Wrestling.
PM SVANidhi
- Ministry – Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
- The PM Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) was launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs on June 01, 2020 for providing affordable Working Capital loan to street vendors to resume their livelihoods that have been adversely affected due to Covid-19 lockdown.
- The duration of the scheme is until March 2022.
- This scheme targets to benefit over 50 lakh Street Vendors.
- A vendor, according to the scheme guidelines is any person engaged in vending of articles, goods, wares, food items or merchandise of daily use or offering services to the public in a street, footpath, pavement etc., from a temporary built up structure or by moving from place to place.
- The goods supplied by them include vegetables, fruits, ready-to-eat street food, tea, pakodas, breads, eggs, textile, apparel, artisan products, books/ stationary etc. and the services include barber shops, cobblers, pan shops, laundry services etc.
Scheme Benefits
- Vendors can avail a working capital loan of up to Rs. 10,000, which is repayable in monthly instalments in the tenure of one year.
- On timely/ early repayment of the loan, an interest subsidy @ 7% per annum will be credited to the bank accounts of beneficiaries through Direct Benefit Transfer on quarterly basis.
- There will be no penalty on early repayment of loan.
- The scheme promotes digital transactions through cash back incentives up to an amount of Rs. 100 per month.
- The vendors can avail the facility of escalation of the credit limit on timely/ early repayment of loan.
Implementation agency
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
Whom to contact
- Nearest Scheduled Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks (SFBs), Cooperative Bank, Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs), Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs) and SHG Banks.
Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat
- Ministry – Ministry of Culture
- The initiative ‘Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat’ was announced by Hon’ble Prime Minister during the Rashtriya Ekta Diva on 31st October, 2015 on the occasion of the 140th birth anniversary of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
- Through this innovative measure, the knowledge of the culture, traditions and practices of different states & UTs will lead to an enhanced understanding and bonding between the states, thereby strengthening the unity and integrity of India.
- Every State and UT in the country would be paired with another State/UT for a year, during which they would carry out a structured engagement with one another in the spheres of language, literature, cuisine, festivals, cultural events, tourism etc.
Key Themes for Interaction:
- To celebrate the idea of India as a nation wherein different cultural units across varied geographies coalesce and interact with each other, this glorious manifestation of diverse cuisine, music, dance, theatre, movies & films, handicrafts, sports, literature, festivals, painting, sculpture etc. will enable people to imbibe the innate chord of binding and brotherhood.
- To make our people aware about the seamless integral hull of the Modern Indian State spread across a vast landmass on whose firm foundations, the geo-political strength of the country is ensured to benefit one and all.
- To impress upon people at large about the increasing inter-connectedness between the constituents of various cultures and traditions, which is so vital for the spirit of nation building.
- To induce a sense of responsibility & ownership for the nation as a whole through these close cross-cultural interactions as it intends to build up the inter-dependence matrix unequivocally.

National Biopharma Mission
- Ministry – Ministry of Science & Technology
- The program named Innovate in India (I3) is an industry- academia collaborative mission of Department of Biotechnology (DBT).
- In collaboration with World Bank for accelerating discovery research to early development of Biopharmaceuticals and to be implemented by Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
- The aim of the mission is to enable and nurture an ecosystem for preparing India’s technological and product development capabilities in biopharmaceutical to a level that will be globally competitive over the next decade, and transform the health standards of India’s population through affordable product development.
The program will specifically focus on the development of new vaccines, bio-therapeutics, diagnostics and medical devices to address the rising burden of diseases in the country.
“JIGYASA” – Student-Scientist connect programme
- The Jigyasa programme is inspired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of a new India and Scientific Social Responsibility (SSR) of Scientific Community and Institutions.
- Jigyasa, a student – scientist connect programme has been launched by the government in New Delhi. The programme would be implemented by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) in collaboration with Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS).
- “JIGYASA” is one of the major initiative taken up by CSIR at national level, during its Platinum Jubilee Celebration Year.
- The focus of this scheme is on connecting school students and scientists so as to extend student’s classroom learning with well planned research laboratory based learning.
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE JIGYASA PROGRAMME
- ‘JIGYASA’ would inculcate the culture of inquisitiveness on one hand and scientific temper on the other, amongst the school students and their teachers.
- The program will also enable the students and teachers to practically live the theoretical concepts taught in science by visiting CSIR laboratories and by participating in projects.
- The Programme is expected to connect 1151 Kendriya Vidyalayas with 38 National Laboratories of CSIR targeting 100,000 students and nearly 1000 teachers annually.
- The focus is on connecting school students and scientists to extend student’s classroom learning with a well planned research laboratory based learning.
- It will also enable the students and teachers to practically live the theoretical concepts taught in science by visiting CSIR laboratories and by participating in mini-science projects.
Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhayay Vigyan Gram Sankul Pariyojana
- Ministry – Ministry of Science & Technology
- This will experiment and endeavour to formulate and implement appropriate S&T Interventions for Sustainable Development through cluster approach in Uttarakhand.
- DST has conceived to adopt a few clusters of villages in Uttarakhand and transform them to become self-sustainable in a time bound manner through the tools of Science and Technology (S&T).
- The key deliverable in this approach is to utilise local resources and locally available skill sets and convert them in a manner using science and technology, that substantial value addition takes place in their local produce and services which can sustain the rural population locally.
- Areas of interventions in these selected clusters would be processing and value addition of milk, honey, mushroom, herbal tea, forest produce, horticulture and local crops, medicinal & aromatic plants and traditional craft and handloom of Uttarakhand.
- Post-harvest processing of Kiwi, Strawberry, Cherry, Tulsi, Adrak, Badi Elaichi through solar drying technology, extraction of apricot oil using cold press technology.
- Stringent product and process control interventions for energy and water conservation would also be ensured through this project.
PM-KUSUM
- Ministry – Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE)
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM) scheme was initiated by Government of India to increase the income of farmers and provide source for irrigation and de-dieselize the farm sector.
- PM-Kusum Yojana got its administrative approval in 8th March 2019 and guidelines were framed in 22nd July 2019.
- This scheme was launched for the installation of solar pumps and other renewable power plants across the nation.
- This scheme is divided into three components which are discussed further.
Objective of PM Kusum Scheme
- Under Kusum scheme Farmers, group of farmers, panchayat, co-operative societies can apply to plant a solar pump.
- The total cost involved in this scheme is divided into three categories in which the Government will help farmers.
- Government will provide a subsidy of 60% to farmers and 30% of the cost will be given by Government in form of loans.
- Farmers will only have to give 10% of the total cost of the project.
- The electricity generated from the solar panel can be sold by the farmers.
- The money gained after selling electricity can further be used for starting a new business.
Three Components of PM-KUSUM Scheme
Component A
- Under this scheme, workers will setup 10,000 MW of decentralized renewable energy power plants which are grid connected on barren land.
- These grids will be setup by farmers, cooperatives, group of farmers, panchayats, Water User Associations (WUA) and Farmer Producer Organizations (FPO).
- Power projects will be setup within the radius of 5 kms of the sub-station.
Component B
- Under this scheme, farmers will be supported to install stand-alone solar agriculture pumps worth of Rs. 17.50 lakh.
- The capacity of the pumps will be up to 7.5 HP for replacement of existing diesel agriculture pumps.
- The capacity can be higher than 7.5 HP but financial support will only be provided uptil 7.5 HP capacity.
Component C
- This scheme is for solarisation of 10 Lakh Grid Connected Agriculture Pumps and individual farmers will be supported to solarize pumps those having grid connected pumps.
- Extra solar power will be sold to Distribution Companies of India (DISCOMs) at pre-fixed tariff.
- Farmer’s irrigation needs shall be met by using the generated solar power.