Russia approves 2nd coronavirus vaccine
- Russia announced that it has granted regulatory approval to another Covid-19 vaccine named EpiVacCorona.
- This comes after the country granted similar approval on Aug. 11 to its first vaccine, Sputnik V, developed by the Moscow-based Gamaleya Institute, after early trials among 76 volunteers were completed.
- The peptide-based, two-shot vaccine, EpiVacCorona, was developed by the Vector Institute in Siberia and tested among 100 volunteers in early-stage, placebo-controlled human trials, which lasted more than two months and were completed two weeks ago.
- The volunteers were between 18 and 60 years old.
- The scientists have yet to publish the results of the study. In comments to the media, scientists developing the vaccine said that it produced enough antibodies to protect the person who had it from the virus and that the immunity it creates could last for up to six months.
- An advanced study involving tens of thousands of volunteers that is necessary to establish safety and effectiveness of the vaccine was scheduled to start in November or December.
- Sputnik V is based on an adenovirus vector and was also registered before Phase III trials. A trial involving 40,000 participants is now under way in Moscow for it.
THE HINDU
Virtual Working Programme For Overseas Professionals
- Dubai has launched a new programme that enables overseas remote working professionals to live in the city while continuing to serve their employers in their home country.
- The move offers remote workers and their families the opportunity to re-locate on an annual basis to the Emirates.
- Remote workers can take advantage of Dubai’s digital infrastructure, connectivity, global networking opportunities and zero income tax for individuals.
- Dubai recently introduced the ‘Dubai Assured’ stamp to certify that establishments have implemented all public health protocols for the prevention and management of COVID-19.
- The programme costs $287 plus medical insurance with valid UAE coverage and processing fee per person.
- Dubai is the first major global destination to fully open up its meetings, incentives, conferences and exhibitions sector internationally, providing opportunities for networking events and face-to-face engagement, which are vital factors in accelerating the revival of key sectors.
THE HINDU
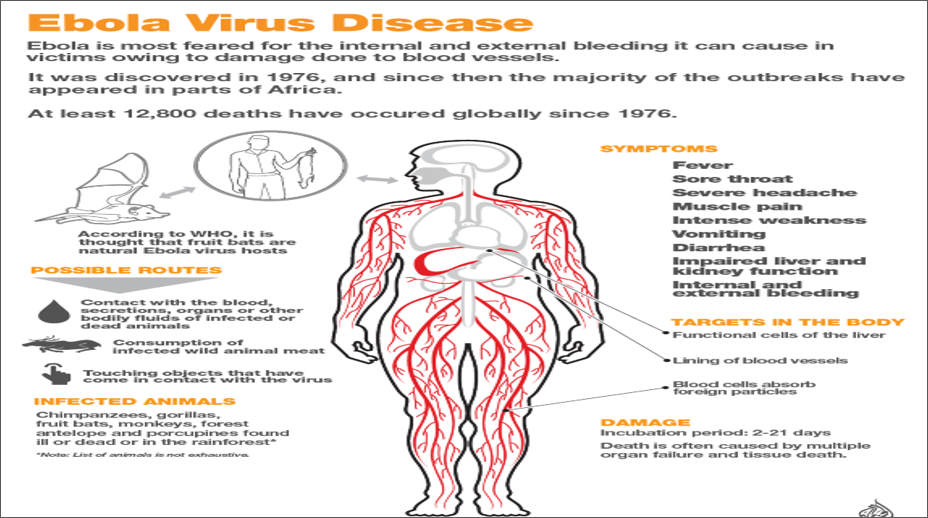
USFDA approves 1st treatment for Ebola
- The The Food and Drug Administration approved the first drug for the treatment of Ebola.
- The US regulator okayed the drug developed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals for treating adults and children. It was tested during an outbreak in Congo that killed nearly 2,300 people before it ended in June.
- The drug, named Inmazeb (IN’-meh-zehb), increased survival in study participants, compared to three other treatments.
- Regeneron’s treatment is a combination of three antibodies that work by killing the virus.
- Seeking U.S. approval first is a common strategy for drugmakers developing treatments for diseases mainly found in the tropics and in developing countries.
- Ebola cases are rare in the U.S., but occasionally are diagnosed in travelers returning from areas with an outbreak.
Facts about Ebola
- Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a disease caused by one of five different Ebola viruses.
- Four of the strains can cause severe illness in humans and animals.
- The fifth, Reston virus, has caused illness in some animals, but not in humans.
- The first human outbreaks occurred in 1976, one in northern Zaire (now Democratic Republic of the Congo) in central Africa: and the other, in southern Sudan (now South Sudan).
- The virus is named after the Ebola River, where the virus was first recognized in 1976, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Ebola is extremely infectious but not extremely contagious.
- It is infectious, because an infinitesimally small amount can cause illness.
- Laboratory experiments on nonhuman primates suggest that even a single virus may be enough to trigger a fatal infection.
- Ebola is considered moderately contagious because the virus is not transmitted through the air.
THE HINDU

Cyprus Scraps ‘golden Passport’ Scheme
- Cyprus has announced the suspension of a “golden passport” scheme to sell citizenship to wealthy investors following a sting by investigative journalists.
- Al Jazeera’s investigative unit filmed high-ranking Cypriot politicians, including the parliamentary speaker, promising to support the sale of a Cypriot passport to representatives of a fictitious Chinese businessman with a money-laundering conviction.
- The citizenship-through-investment scheme, which has been in operation in its current form since 2013, allowed foreign individuals to invest €5m (£2.26m) in the country in exchange for citizenship, raising a reported €7bn to sustain the country’s sclerotic economy.
- But it has for years been the target of ferocious criticism by anti-corruption campaigners, who have repeatedly warned that such schemes can be used by criminal individuals and organisations to launder large sums of corrupt funds into property.
- Other countries to run controversial “golden visa” or “golden passport” schemes include the UK, Portugal and Malta.
What are golden passports?
- They are schemes which essentially allow rich foreign investors to buy citizenship, or long-term residency rights, in a country.
- For instance Cyprus offers citizenship within six months to those who invest €2m in local real estate. There is no language requirement or interview required. For permanent residency an investment of just €300,000 is required.
- There are similar schemes offered by countries ranging from Antigua to Bahrain, from Malaysia to Panama.
- But it’s not just small countries which offer residency-for-cash. Canada has an “immigrant investor program” available for those with a net worth of at least $1.6m and a $800,000 investment.
- Even the UK has a special visa available for those who invest £200,000 in a UK business, although this doesn’t come with a passport.
THE GUARDIAN
India re-elected as president of International Solar Alliance
- India and France were re-elected as president and co-president of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) for a term of two years at its third assembly.
- The Third Assembly of the ISA was attended by 34 members’
- As many as 53 member countries and five signatory and prospective member countries participated in the assembly.
- Four new vice-presidents were also chosen to represent the four regions of the ISA.
- The representatives of Fiji and Nauru for Asia Pacific Region; Mauritius and Niger for Africa Region; UK and the Netherlands for Europe and Others Region; and Cuba and Guyana for Latin America and Caribbean Region assumed the vice presidency.
- The assembly also approved the initiatives of the ISA Secretariat in institutionalising ISA’s engagement with the private and public corporate sector through the Coalition for Sustainable Climate Action (CSCA).
- Solar energy is already contributing around 2.8% of global electricity, and if trends were to continue, by 2030, solar will become most important source of energy for electricity production in large part of the world.
- The ISA has aggregated a demand for more than 270,000 solar pumps across 22 countries, more than 1 GW of solar rooftop across 11 countries, and more than 10 GW of solar mini-grids across nine countries under its respective programmes.
- France has also supported the collaboration with the World Bank to mobilise financing.
- A facility ‘Sustainable Renewables Risk Mitigation Initiative’ (SRMI) should help mobilize 18 billion euros in private investment to finance more than 10 gigawatts of solar projects.
- The first project is being launched in Mozambique with the support of France and the European Union.
- under the framework of the ISA Star-C programme, the French National Institute for Solar Energy (INES) will very soon launch a specific program for the small island states of the Pacific.
- The ISA assembly was also presented with the report prepared by the World Resources Institute (WRI).
- The report identifies the sources of funds, opportunities and constraints, in scaling up solar investments and the contribution of ISA in assisting member countries.
- The assembly welcomed the move of the ISA to work with WRI to develop a roadmap for mobilisation of $1 trillion by 2030.
- The Kingdom of the Netherlands, Bloomberg Philanthropies, Bloomberg New Energy Finance and Climate Works Foundation providing the required financial and technical assistance for preparation of the roadmap.
- The roadmap will also analyse the potential for mobilising further investments in solar energy going beyond solar power projects to solar energy applications in transportation and cooling and heating and for implementing the vision of ‘One Sun, One World, One Grid’
- In the wake of the global pandemic, ISA responded by setting up ISA CARES, an initiative dedicated to deployment of solar energy in the healthcare sector.
- The initiative aims to solarise one primary health sector in each district of target member countries.
- The membership of the ISA has continued to grow since the Second Assembly in 2019. The ISA is now supported by 68 member countries, and a further 20 countries are in the process of becoming members.
- The ISA is an initiative that was launched by the Prime Minister of India and the President of France on November 30, 2015 in Paris on the side-lines of the COP-21.
- The overarching objective of the ISA is to collectively address key common challenges to the scaling up of solar energy in ISA member countries.
THE HINDU
Cooperation In Sustainable Groundwater Management
- The Union Cabinet approved a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Australia
- to promote cooperation in surface and groundwater training, education and research to achieve water security for agricultural, urban, industrial and environmental purposes.
- The MoU was signed between Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga rejuvenation, India and Managing Aquifer Recharge and Sustaining Groundwater use through village-level intervention (MARVI) PARTNERS, Australia in October 2019.
Cabinet Approves Stars Project To Improve School Education
- The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister has approved implementation of the Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States (STARS) project with a total project cost of over Rs5,700 crore.
- Of this amount, the World Bank will fund approximately Rs3,700 crore.
- STARS project would be implemented as a new centrally sponsored scheme under Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Education (MoE).
- The project covers six states, namely Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala and Odisha. The identified states will be supported for various interventions for improving the quality of education.
- Besides this project, it is also envisaged to implement a similar ADB-funded project in five states, namely Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand and Assam.
- All states will partner with one other state for sharing their experiences and best practices.
- The STARS project seeks to support the states in developing, implementing, evaluating and improving interventions
- with direct linkages to improved education outcomes and school to work transition strategies for improved labour market outcomes.
- The overall focus and components of the STARS project are aligned with the objectives of National Education Policy (NEP)-2020 of Quality Based Learning Outcomes.
- The project envisions improving the overall monitoring and measurement activities in the Indian School Education System through interventions in selected states.
- The project shifts focus from the provision of inputs and maintaining of outputs to actual outcomes by linking the receipt and disbursement of funds to these outcomes.
PIB
“Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojna”
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare launched the second phase of “Thalassemia Bal Sewa Yojna” for the underprivileged Thalassemic patients.
- Launched in 2017, this scheme is a Coal India CSR funded Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) program that
- aims to provide a one-time cure opportunity for Haemoglobinopathies like Thalassaemia and Sickle Cell Disease for patients who have a matched family donor.
- The CSR initiative was targeted to provide financial assistance to a total of 200 patients by providing a package cost not exceeding Rs. 10 lakhs per HSCT.
- The Union Health Ministry has initiated a project to provide treatment to 200 children suffering from thalassaemia in the current financial year with Coal India funding it.
- The government has identified four hospitals across the country where bone marrow transplant along with post-surgery treatment will be carried out.
- The cost of the total procedure is Rs 10 lakh and it will be borne by Coal India.
- Only patients whose monthly family income is below Rs 20,000 will be eligible for this assistance.
- An estimated 10,000 to 12,000 children are born with thalassaemia every year in the country.
- The only curative treatment for these children is bone marrow transplant which is quite an expensive and costs around 22-25 lakhs in private facilities.
- Haemoglobinopathies, such as Thalassemia and sickle cell disease are inherited disorders of red blood cells and are preventable.
- These illnesses are chronic, life impairing and in some cases, life threatening and impose a heavy emotional and financial burden on families.
- In India, Thalassemia Major (TM) and the severe form of Thalassemia Intermedia (TI) constitute the major burden of disease.
- Both are commonly managed by regular lifelong blood transfusions and regular iron chelation.
- These Thalassemia syndromes are caused by inheritance of abnormal (beta) Thalassemia genes
- from both parents or
- abnormal beta-Thalassemia gene from one parent and abnormal variant haemoglobin gene (HbE, HbD) from the other parent.
PIB
MSMEs ministry pushing Industry 4.0
- CHAMPIONS, a single-window portal to assist micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India launched by the MSME Ministry,
- has deployed artificial intelligence (AL) and machine learning (ML) solutions to strengthen its mandate for the benefit of enterprises, boosting the B2B network.
- The Ministry is also gearing up for Industry 4.0 by transforming CHAMPIONS a robust sectoral digital platform.
- The portal (champions.gov.in), developed in-house by the Ministry, has been operational since June 1, 2020.
- The digital platform has been integrated with ‘physical control rooms’ or ‘digital war rooms’ spread across as many as 69 locations in the country, emerging as one of the front runner platforms for the MSMEs.
CHAMPIONS: Phase-I Approach
- The phase-1 operations, powered by AL and ML solutions that began on October 14, 2020,
- focuses on social media insights related to the MSMEs for its policy matters through Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and other sources, including online news.
- These insights were not available to the Ministry in a holistic manner and are now accessible.
- This will help the Ministry to prepare data for analysis, thus freeing up the Ministry’s staff to engage in more productive work.
- The phase-1 of CHAMPIONS has been powered by Intel, which has guided the Ministry for the last five months in implementing tools of AL and ML.
- The concept, scope analysis and design has been built in-house by the Ministry with the help of the National Informatics Centre (NIC), Government of India.
Future Roadmap
- The roadmap for next phase-2 will include real-time grievance redressal and management.
- Increasing the performance of control rooms and officers through AI enabled Chat Bots for faster response to the query of portal users and for effective resolution and greater stakeholder satisfaction.
- The objective of CHAMPIONS (Creation and Harmonious Application of Modern Processes for Increasing the Output and National Strength) is to help the MSMEs in terms of finance, raw materials, labour and permissions and the MSMEs to capture new opportunities in manufacturing and services sectors.
IE
GOLD STEVIE® AWARD
- Seema Gupta, Director (Operations), Power Grid Corporation of India Limited, a PSU under Ministry of Power, has been named the winner of GOLD Stevie® Award in the LIFETIME ACHIEVEMENT- BUSINESS category in the 17th annual Stevie Awards for Women in Business.
- The Stevie Awards for Women in Business honour women executives, entrepreneurs, employees, and the companies they run–
- The Stevie Awards have been hailed as the world’s premier business awards.
- For this year, the Gold, Silver, and Bronze Stevie Award winners were determined by the average scores of more than 180 business professionals around the world, working on seven juries.
- This global recognition is yet another achievement in Mrs. Seema Gupta’s illustrious career.
- She has been earlier conferred with Special Commendation Award for Outstanding Women Manager in Public Sector Enterprises by the Honourable President of India in 2017 and was adjudged as the Best Contributor at the ITOMS 2018 Conference in Malaysia.
About POWERGRID
- POWERGRID, one of the largest power transmission companies globally, is a Maharatna CPSE under the administrative control of Ministry of Power, Govt. of India and is the Central Transmission Utility of India.
PIB
Zojila tunnel
- Union Minister Nitin Gadkari launched the first blasting for construction related work at the 14.15 km Zojila tunnel, one of the longest in Asia, that will provide all-year connectivity between Srinagar valley and Leh.
- The project holds strategic significance as Zojila Pass is situated at an altitude of 11,578 feet on the Srinagar-Kargil-Leh National Highway and remains closed during winters due to heavy snowfall.
- At present it is one of the most dangerous stretches in the world to drive a vehicle and this project is also geo-strategically sensitive.
- Blasting means blowing up or breaking apart something solid with explosives.
- The tunnel will provide all-weather connectivity between Srinagar valley and Leh (Ladakh plateau) on NH-1, and will bring about an all-round economic and socio-cultural integration of Jammu & Kashmir.
- It involves construction of a 14.15-km long tunnel at an altitude of about 3,000 m under Zojila pass (presently motorable only for six months in a year) on NH-1 connecting Srinagar and Leh through Drass and Kargil.
- The project was re-awarded this year to Megha Engineering & Infrastructure Ltd (MEIL).
THE HINDU
International Day of Rural Women – 15 October
- The International Day of Rural Women was created in 1995 by Civil society organizations at the Fourth World Conference on Women in Beijing and was declared an official UN Day in 2007 by the UN General Assembly.
- Theme: “Building rural women’s resilience in the wake of COVID-19”, for “building back better” by strengthening rural women’s sustainable livelihoods and wellbeing.
- Rural women play a crucial role in agriculture, food security and nutrition, land and natural resource management, and rural enterprises.
- They have been at the front lines of responding to the pandemic even as their unpaid care and domestic work increased under lockdowns, mobility is restricted, supply chains are disrupted, and climate and conflict crises compound COVID-19 impacts.
- In India, millions of rural women organized in self-help groups have helped to fill acute shortages and gaps by producing masks and hand sanitizers, providing fresh food through community kitchens, offering financial services, and communicating vital COVID-19 information in rural communities.
UN
India designated Vice-Chair of OECD Working Group on GLP
- India has been designated the ‘Vice-Chair’ of Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) Working Group of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), recognising the contribution of the Indian GLP programme.
- Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) is a quality system, which has been evolved by Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- to ensure that safety data generated on various chemicals like industrial chemicals, pharmaceuticals (Human and Veterinary), agrochemicals, cosmetic products, food/ feed additives, and medical devices, etc., can be relied upon by regulatory authorities.
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, established the National GLP Compliance Monitoring Authority (NGCMA) with the approval of the Union Cabinet on April 24, 2002.
- NGCMA is the National body which grants GLP certification to test facilities (TFs) conducting safety studies on new chemicals of the above-mentioned categories
- in accordance with OECD Principles of GLP and OECD Council norms. The Grant of the first GLP certificate by NGCMA in 2004 was a milestone.
- The non-hazardous nature of chemicals needs to be established through studies and data, which is examined by the regulators of the concerned countries
- to certify that the use of these chemicals does not pose any hazards to human health and the environment.
- On March 3, 2011, India became full adherent to the Mutual Acceptance of Data (MAD) in the OECD.
- The MAD status has given global recognition to India’s non-clinical safety data by tremendously augmenting its credibility and acceptability across the globe.
- The spectrum of activities of Indian GLP TFs is wide, involving eight (8) types of chemicals/test items and nine (9) areas of expertise.
- The National GLP program has not only helped to build a network of GLP TFs in the country but also created a huge quantum of highly competent human resources.
PIB
Madhuca diplostemon
- A tree species, long believed extinct, has been rediscovered after a gap of more than 180 years from a sacred grove in Kollam district.
- Scientists at the Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute (JNTBGRI) at Palode here have identified the tree as Madhuca diplostemon (family Sapotaceae), a threatened species of the Western Ghats whose specimen was first collected in 1835.
- Locally, it was erroneously believed to be the common Attilippa.
- Since the species is represented only by one specimen in a single locality, it is eligible to be categorised ‘Critically Endangered’ by the IUCN.
- Madhuca diplostemon has an interesting history. In 1835, Robert Wight, a surgeon-botanist with the East India Company, had collected three specimens.
- In 1848, he described it as Diospyros obovata in his famous work, the Icones Plantarum Indiae Orientalis.
- Later C.B. Clarke corrected it as Isonanandra diplostemon and, in 1960, P. Royen described it as Madhuca diplostemon.
- The JNTBGRI is planning to undertake the ex situ conservation of this species through the institute’s species recovery programme.
THE HINDU
Conservation of one-horned rhinoceros
- In conservation efforts for the greater one-horned rhinoceros population in India, the latest strategy is an examination of rhino dung to understand health issues of the animal.
- Since 2017, the Rhino Task Force of Assam and World Wildlife Fund India (WWF India) have been undertaking steps to study pathogens found in fresh rhino dung samples in Assam, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
- WWF India has recently published preliminary reports — ‘Prevalence of Endoparasitic Infections in Free-Ranging Greater One-Horned Rhinoceros’ — for Assam and West Bengal.
Why is such a project important?
- While poaching is believed to be the main cause of death in rhinos, rhinos also die of natural causes which have not been studied in great detail.
- According to the researchers, habitat degradation can lead to an increased exposure to pathogens.
- “Due to increasing livestock pressure on protected areas, there is a possible threat of pathogens getting transferred from domestic animals to wild animals.”
How is the project being carried out?
- Till date, there has been no systematic study on the prevalence of disease-causing parasites and diseases caused by these in the rhino population in India.
- “In order to address this knowledge gap, the present study is a part of a series that involves screening of pathogens through a non-invasive method of dung sample analysis”.
- Samples were collected from UP’s Dudhwa National Park; West Bengal’s Jaldapara National Park and Gorumara National Park; and Assam’s Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park, Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, Manas National Park, and Kaziranga National Park.
- The researchers collected the samples fresh (not older than from the previous night), gave them unique IDs and sent them to the Department of Parasitology in the College of Veterinary Science, Assam Agricultural University, Guwahati.
What are the findings?
- From the samples from Assam and West Bengal, the study concluded that parasites from four genera were present in an estimated 68% of India’s rhino population.
- The overall prevalence of endoparasites was 58.57% in Assam and 88.46% in West Bengal; results from UP are pending.
- The endoparasites in Assam belonged to four genera: Amphistome spp, Strongyle spp, Bivitellobilharzia nairii and Spirurid spp, while West Bengal reported the prevalence of only Strongyle spp, Assam reported all four.
- These pathogens are quite common and not very alarming.
- The team will now branch out to examine bacterial fauna and viral agents, as well as a hormonal study.
IE
Lgbt Groups In Japan Launch Petition Seeking Equality Law
- Sexual minority groups and human rights activists launched a petition calling for an LGBT equality law in Japan in hopes that it can be enacted next year, when the country is to host the Olympics and will be the focus of international attention.
- Japan has slowly shown an increased awareness of sexual diversity but it is often superficial.
- Pressure to conform still forces many lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people to hide their sexual identities, even from their families.
- Same-sex marriage is not legally allowed, and transgender people are required to remove their reproductive organs to have sex changes reflected in official documents — a requirement that international medical experts and human rights groups criticize as inhumane.
- Recently, a local assemblyman in Tokyo belonging to Prime Minister Yoshihide Suga’s conservative governing party sparked outrage
- after linking LGBT people to the country’s declining birthrate, saying constituents in his ward would go extinct if sexual minorities are protected.
- Last year, Shiho Shimoyamada, a soccer player for the Japanese women’s football club Sfida Setagaya, disclosed that she has a same-sex partner, becoming the first prominent Japanese athlete to do so.
- Japan ranks among the lowest among OECD countries in LGBT equality, and does not even have a population estimate for sexual minorities.
THE HINDU
Deleting ‘ineligible’ Names In Assam’s NRC
- Recently, the National Register of Citizens (NRC) authorities in Assam have ordered the deletion of “ineligible” names that had erroneously made it into the prepared register.
Whose names will be deleted?
- “some names of ineligible persons” — persons ‘declared as foreigners’ (DF) by Foreigners Tribunals, persons marked as ‘Doubtful Voters’ (DV) by election officials, or persons whose cases are ‘pending at Foreigners Tribunals’ (PFTs), and their descendants — had “found entry to the NRC”.
- Foreigners Tribunals (FTs) are quasi judicial bodies meant to give opinion on whether a person is an “illegal foreigner” as per The Foreigners Act, 1946.
- They send notices to people who are referred to them by the Border Police, or who have been marked as ‘D’ (doubtful) voters by the local election office.
- As per the laws governing the preparation of the NRC, persons falling in the above categories cannot be included in the NRC.
But if these individuals were declared ‘foreigners’, how could they have made it into the NRC?
- One explanation that is offered is that such persons may have got their names included using fraudulent documents and by deceitful means.
- The other reason that officials often cite is that there is no synchronised real time database, which reflects the status of a suspected ‘foreigner’ to the NRC officials.
- Therefore, an official on the ground may actually have no way of knowing that a particular applicant has earlier been declared a ‘foreigner’ by an FT.
Is there a political context to the new announcement about the “ineligible” names and the deletions?
- The state government has maintained that a 10%-20% re-verification is necessary to get a “correct”
- The Assam government has reiterated that it sticks to its demand of re-verification — 20% in border districts and 10% elsewhere — of the included names in the final NRC.
So where does the NRC stand now?
- The NRC process has hit a wall as of now since the rejection orders to the 19 lakh excluded persons — which will allow them to appeal against the exclusion in the Foreigners’ Tribunals — is yet to be issued.
- Officials have cited the Covid-19 pandemic as well as discrepancies in some rejection orders, which need to be re-checked, as reasons for the delay.
- Meanwhile, without the rejection order, the excluded persons are stuck in a limbo.
- The Supreme Court, which had proactively supervised the process from 2013 onward, has not heard the matter since January 6.
IE
Holographic Imaging To Detect Viruses And Antibodies
- Scientists have developed a method using holographic imaging to detect both viruses and antibodies.
- If fully realised, this proposed test could be done in under 30 minutes, is highly accurate, and can be performed by minimally trained personnel.
- Developed by scientists from New York University, the method uses laser beams to record holograms of their test beads.
- The surfaces of the beads are activated with biochemical binding sites that attract either antibodies or virus particles, depending on the intended test.
- Binding antibodies or viruses causes the beads to grow by a few billionth parts of a metre.
- Researchers have shown they can detect this growth through changes in the beads’ The test can analyse a dozen beads per second.
- This can mean cutting the time for a reliable thousand-bead diagnostic test to 20 minutes.
- The holographic video microscopy is performed by an instrument, xSight, created by Spheryx.
IE
New Shephard, the rocket system built by Blue Origin
- A rocket system meant to take tourists to space successfully completed its seventh test launch after it took off from a test facility in Texas.
- Called New Shephard, the system is built by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos’s space company called Blue Origin and will eventually allow space tourists to experience microgravity by taking them over 100 km above the Earth.
- In 2018, Blue Origin was one of the ten companies selected by NASA to conduct studies and advance technologies to collect, process and use space-based resources for missions to the Moon and Mars.
- In 2019, both signed an agreement that gives Blue Origin permission to use NASA’s historic test stand, as a part of a growing number of partnerships between the space agency and the commercial space industry.
So, what is New Shephard?
- New Shephard has been named after astronaut Alan Shephard, the first American to go to space, and offers flights to space over 100 km above the Earth and accommodation for payloads.
- Essentially, it is a rocket system that has been designed to take astronauts and research payloads past the Karman line – the internationally recognised boundary of space.
- The idea is to provide easier and more cost-effective access to space meant for purposes such as academic research, corporate technology development and entrepreneurial ventures among others.
How does it work?
- The rocket system consists of two parts, the cabin or capsule and the rocket or the booster.
- The cabin can accommodate experiments from small mini payloads up to 100 kg.
- As per Blue Origin, the mini payloads provide easier space access to students, who are part of educational institutions that are developing their own space programs, “for less than the price of new football uniforms”.
- Further, the cabin is designed for six people and sits atop a 60-feet tall rocket and separates from it before crossing the Karman line, after which both vehicles fall back to the Earth.
- The system is a fully reusable, vertical takeoff and vertical landing space vehicle that accelerates for about 2.5 minutes before the engine cuts off.
- After separating from the booster, the capsule free falls in space, while the booster performs an autonomously controlled vertical landing back to Earth.
- The capsule, on the other hand, lands back with the help of parachutes.
What was the test launch about?
- During the seventh launch on Tuesday referred to as NS-13, there were 12 payloads onboard including the Deorbit, Descent and the Landing Sensor Demonstration under the NASA Tipping Point partnership.
- The lunar landing sensor demo, for instance, was the first payload to be mounted onto the exterior of the space vehicle and was meant to test the technology that helps to achieve high accuracy landings such as those done on the lunar surface.
- Technologies such as these are supposed to aid long-term lunar explorations and future missions to Mars.
IE
E.U. leaders divided over new climate goals for 2030
- European Union leaders remain divided about a more ambitious target for cutting greenhouse gas emissions and will not reach an agreement at their summit.
- This summit only start discussing the proposal to reduce emissions by at least 55 % by 2030.
- The goal is to reach an agreement in December ahead of the adoption of the first ever European climate law.
- In proposing a reduction target of at least 55 % by 2030 compared with the current target of 40 %, EU commission President Ursula von der Leyen predicted in September that the new target would be too much for some and not enough for others.
- Supported by Germany, Von der Leyen’s revised target needs to be endorsed by the 27 EU countrie to make it legally binding.
- Recently, a group of 11 countries including Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Ireland, Latvia, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain and Sweden embraced her ambition in a joint statement published ahead of the summit in Brussels.
- While the European Parliament pushes for an even greater 60 % reduction in emissions, some eastern EU countries that depends on coal for much of their energy needs are less enthusiastic.
- They worry about the social, environmental and economic costs of the transition to a greener economy.
- Poland last year did not commit to the EU’s 2050 climate neutrality goal and is asking for more details about the measures.
- World leaders agreed five years ago in Paris to keep global warming below 2 degrees Celsius (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit), ideally no more than 1.5 degrees C (2.7 F) by the end of the century.
- Scientists say countries will miss both of those goals by a wide margin unless drastic steps are taken to begin cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
- Under the Paris Agreement, countries are due to submit updated climate targets by the end of the year.
THE HINDU
Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) report
- Corporate and business houses donated ₹10 crore to five national parties in 2018-19.
- The biggest share of over ₹698 crore went to BJP, according to the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR).
- Such donations amounted to 92% of the contributions to political parties from known sources and it increased by 131% between 2004-12 to 2018-19.
- The parties considered in the report are the BJP, the Congress, the NCP, the CPI(M) and the Trinamool Congress.
- Though a national party, the BSP has not been considered as it has declared that it received no voluntary contributions above ₹20,000 since 2004.
- The CPI did not declare any income from corporates for 2018-19.
- The national parties received the highest amount in 2018-19 (the period which preceded the Lok Sabha elections), followed by ₹18 crore in 2014-15 (during which the 16th Lok Sabha elections were held) and ₹563.19 crore in 2016-17.
- Between 2012-13 and 2018-19, donations from corporates to national parties increased by 968%, with a drop in the percentage in 2015-16.
- 15 categories identified
- The ADR report identifies 15 categories of corporate donors. Of the contribution to the five national parties, ₹54 crore was from the unsegregated category, which includes companies with no details available online or whose nature of work is unclear.
- While electoral trusts were the biggest donors, with a share of 69.93%, manufacturing sector was the second highest with the contribution of ₹85 crore.
- The ADR has recommended that no part of the Form 24A, submitted by the parties to provide details of donations above ₹20,000, should be left blank.
- All such donors should provide PAN details. Any party which does not submit its donation statement to the EC on or before October 31 should be heavily penalised and its income should not be tax-exempted.
THE HINDU
Robotic Plant Buggy Can Scan Crops, Gather Data
- Google’s parent Alphabet has developed a robotic plant buggy to scan crops and generate data to help farmers grow food.
- The US-based company developed a low-emission electric powered plant buggy fitted with solar panels that can roll through the fields, scanning crops and collecting high quality images of each plant.
- The images are combined with satellite imagery, weather data, and soil information, to get a clear picture of the happenings in the field.
- The buggy collects plant-level data, and the robotics, sensing and software tools collect and interpret diverse data from the field.
- The company believes that the current tools do not help farmers understand agriculture’s complexity and take effective decisions.
- The new tool collecting important data from the field, like plant height, leaf area and fruit size, can help farmers predict size and yield of their crop, enabling them to make better yield projections.
- The company used machine learning to spot patterns about how plants grow and interact with their environment.
- The buggy comes in different shapes and sizes so that it can adapt to fields with different crops.
- It has plant mapping and identification GPS software to locate plants.
- Its sophisticated cameras and machine perception tools can spot issues in the field and analyse plant traits.
THE HINDU